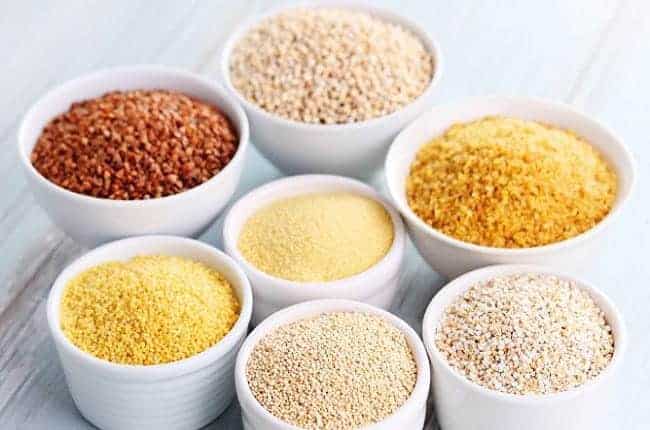
Types and properties of groats
Groats are a product that is very often recommended by nutritionists and personal trainers. Due to the large amount of good carbohydrates and the multitude of nutrients, groats are considered to be one of the best foods. They can also be used in a variety of ways: as a substitute for potatoes for dinner, as an ingredient in salads or even in tasty desserts. What is more, there are many types of groats and each of them is characterized by individual values and health properties. Let’s find out what the most popular groats are and what properties they have.
Contents
Why bet on groats?
There are several reasons why it is worthwhile to introduce groats into your diet. One of them is, of course, the interesting flavour – each of the groats has a different note and goes well with different products. Groats also provide our body with a wealth of vitamins and minerals, such as zinc, magnesium, potassium and B vitamins. Groats are a great source of complex carbohydrates and protein, components that are extremely important in the diet of an athlete. In addition, some types of groats are gluten-free, so they also work well in the diet of people with celiac disease.
Let’s see which groats are best to implement into your diet.
Check: Oatmeal diet – what does it consist in?
Buckwheat groats

Buckwheat groats are made from buckwheat seeds. It is available in two types:
- roasted buckwheat groats – characterised by dark colour and intensive taste;
- unroasted buckwheat groats (white) – considered to be healthier.
Properties of buckwheat groats
- is gluten-free, thanks to which it can be consumed by people with coeliac disease;
- contains a large amount of antioxidants, which makes it beneficial to the nervous system and blood vessels;
- is rich in vitamins, including: B9, B2, B6, and B5;
- has a lot of minerals: iron, potassium, magnesium, zinc, manganese, selenium and copper.
Contraindications of buckwheat groats
Buckwheat groats should not be consumed by people:
- with kidney failure;
- suffering from stomach or duodenal ulcers;
- children under 10 months of age.
Buckwheat groats – uses in the kitchen
- It goes well with meat and sauces, e.g. in goulash;
- combined with white cheese can be used as an ingredient of stuffing for dumplings or pancakes;
- ideal as stuffing for vegetables;
- great for chops;
- ground can be used in baking.
Buckwheat groats

Produced from millet grain. It is characterised by small grains with a yellow colour. It is considered by nutritionists to be one of the best groats available.
Properties of millet groats:
- does not contain gluten;
- contributes to good condition of bones, joints, nails, skin and hair due to high content of silicon and iron;
- helps to maintain acid-base balance;
- is rich in minerals: iron, magnesium, copper, zinc, selenium, manganese;
- contains vitamins of group B (B1, B2, PP, B6, B9, and B5) vitamin E;
- is easily digestible.
Contraindications of millet groats
It should not be consumed more than once a week by people with hypothyroidism.
Use of blue groats in cooking
- Ideal for meat and vegetable dishes;
- Great as an ingredient in tasty and healthy desserts;
- Complements well with yoghurt;
- is an ideal idea for energetic breakfast.
Barley groats

Obtained from barley grains. On the basis of the grinding degree it can be divided into
- barley groatspearl barley – full, polished grain, devoid of husks only;
- Pearl barley groats – pearl barley groats cut into pieces, available in coarse, medium and fine forms
- broken barley groats – crushed pearl barley, which has not been polished, thanks to which it has retained more nutritional components.
Properties of barley groats:
- supports the treatment of cardiovascular diseases;
- recommended for people suffering from hypertension;
- helps to normalize blood glucose level;
- is a good source of fibre and protein;
- contains minerals: iron, potassium, magnesium, zinc, copper, manganese, selenium
- is a source of vitamins B1, B2, PP, B6.
Barley groats – contraindications
Barley groats should not be consumed by people with coeliac disease and children under 10 months of age.
Use of barley groats in cooking
- Ideal for stews and vegetable and meat sauces;
- It tastes great with various kinds of soups;
- excellent for stuffed cabbage rolls or as a filling for vegetables;
- good addition to vegetable and fruit salads;
- best for porridge;
- suitable for chops.
Amaranthus

It is a fine groat, called amaranth. It is considered one of the oldest cultivated plants in the world. It is recommended in the diet of athletes due to its high content of well-absorbed proteins.
Nutritional values of amaranth:
- contains a fair amount of well-absorbable protein;
- is a rich source of iron;
- does not contain gluten.
Amaranth in the kitchen – application
Amaranth is most often used for baking and sweet desserts. In stores you can also find expanded amaranth, which is perfect as an addition to yoghurts, muesli and oatmeal.
Check also: Roman cumin – how does it affect our figure?
Quinoa

Otherwise known as quinoa, it has been cultivated for years, yet in the modern diet kitchen it appeared relatively recently. It belongs to the group of products counted among the healthiest, which is why athletes and specialists in healthy nutrition like to use it.
Nutritional properties of quinoa:
- has an antioxidant effect;
- soothes inflammation;
- shows anti-allergic properties;
- contains no gluten.
Quinoa use in cooking
Quinoa has a very wide application in the kitchen. It is often used as an addition to other groats, it is commonly encountered in yogurts, can be used as an addition to baked goods and desserts.
Semolina

White, fine groats, which are made in the process of grinding wheat into flour. It is very easy to prepare and loved by children.
Porridge properties
- contains vitamins: B1, B2, B6, B9, B5, PP;
- has a lot of minerals: potassium, magnesium, zinc, iron, manganese, copper;
- contains a large amount of iodine;
- is easily digestible.
Wheat groats – use in cooking
It is mostly used for thickening soups and other dishes. It is an excellent addition to desserts. It is most popular served with milk and fruit.
Couscous

Light yellow, small groats made from durum wheat. Its grains are steamed and polished. It is quite popular not only for its nutrients, but also for its quick preparation. It is usually enough to pour boiling water over it and wait 5 minutes to be ready for consumption.
Properties of couscous
- It is easily digestible;
- contains minerals: B1, B2, B5, PP, B6 and B9 and folic acid;
- it is a rich source of protein and carbohydrates;
- It is characterized by a lower amount of fat in comparison with other groats.
Couscous contraindications
Due to its gluten content, couscous is not recommended for people suffering from coeliac disease and children under 9 months old.
Couscous – culinary applications
It tastes great sweet when added to yogurt, muesli and other desserts. Used in baking. Suitable for meat dishes, goes well with meat sauces and vegetables.
Bulgur groats

Bulgur groats are made from cooked, dried and crushed grains of durum wheat. It comes in three varieties:
- fine-grained;
- medium grain;
- coarse-grained.
Properties of bulgur groats
- It supports the work of cardiovascular system;
- has a beneficial effect on the nervous system;
- contains minerals: calcium, magnesium, iron, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, zinc;
- is a source of vitamins: A, E, K, B6, folic acid, niacin, riboflavin;
- helps digestion.
Bulgur groats – contraindications
Bulgur groats contain gluten, so they are not recommended for people with gluten intolerance.
See also: Soup diet – can it help you lose weight?