Vitamin A – medicinal and cosmetic properties you can trust
There is no exaggeration in comparing the human body to a complex factory, after all, we function through the work of many equally important organs and internal systems. For this to run smoothly, we need to take care of the right fuel, the daily supply of the body with the right doses of nutrients, of which vitamins are the most important. From several previous entries we could learn about the properties and action of vitamins B, C and D, among others, but we still know nothing about vitamin A, also essential for our health.
Contents
- 1 Vitamins – what they actually are
- 2 Vitamins – how they are divided
- 3 Vitamins – functions performed in the body
- 4 Vitamin A – a mixture of several valuable compounds
- 5 Vitamin A – natural sources
- 6 Vitamin A – effects of deficiency or excess and proper dosage
- 7 Vitamin A – the most important therapeutic properties
- 8 Vitamin A – dietary supplements that contain it
Vitamins – what they actually are
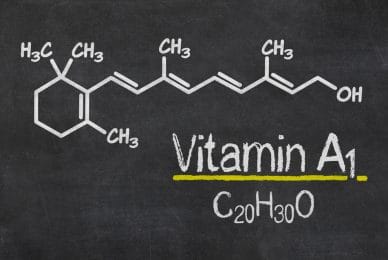
However, before we get into describing the properties of vitamin A, we should know what they are, when they were discovered, who did it and what function they perform in the body. Vitamins, including vitamin A, are a large group of organic, low-molecular compounds, without which many processes in the human body could not function properly. They were first isolated by our compatriot Kazimierz Funk in 1913 and also created their name coming from two Latin words, vitae, meaning life, and amina, meaning amine group.
Vitamins – how they are divided
All known vitamins, and there are as many as 13 of them, are divided according to the most popular criterion, which is the type of substances in which they dissolve, obtaining two basic groups:
1. water-soluble vitamins
Their characteristic feature is that they are not stored in the body, so we must constantly replenish all deficiencies, and the group of water-soluble vitamins includes:
- Vitamin B – types, effects and health properties
B vitamins, such as: thiamine (B1), riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), pantothenic acid (B5), pyridoxine (B6), Biotin – properties, uses, sources. Biotin for hair, skin and nails biotin (B7), Folic acid – properties properties and role in the body Folic acid (B9), Vitamin B12 – action, properties, role in the body. Symptoms of deficiency cobalamin or cyanocobalamin (B12); - Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) – properties. What do we need it for?
vitamin C, or ascorbic acid.
2. fat-soluble vitamins
Which are deposited and stored in fat tissue, but in this case you may experience symptoms of excess deposited in too large amounts. This group of vitamins includes:
- Vitamin A, otherwise known as beta-carotene, retinol, or provitamin A;
Vitamin D – properties and dosage. What are the symptoms of vitamin D deficiency and excess? vitamin D, calciferol; - vitamin E, a-tocopherol;
- vitamin K, phytomenadione.
Vitamins – functions performed in the body
Among the many nutrients that our body requires throughout life, vitamins, and from all groups, invariably occupy a prominent place. Of course, no one here discounts the importance of other substances, minerals, fats, carbohydrates, or proteins. However, a deficiency of a vitamin from any group immediately affects the state of health, significantly worsening it. With the right daily dose of vitamins, we can count on:
- regulation of many processes How to speed up metabolism to lose weight – 5 simple tips
metabolic occurring in cells; - proper blood flow and blood clotting;
- improved functioning of the heart and the entire circulatory system
- removal of dangerous free radicals from the body, many of the vitamins are antioxidants – an effective barrier against free radical attack antioxidants;
- good eyesight, as they are responsible for proper vision;
- healthy, firm skin without Acne – causes, symptoms and most common treatments acne and other diseases, thanks to more efficient production Collagen – causes and effects of deficiency. Collagen sources
collagen; - a more efficient nervous system, good memory and concentration;
- proper levels of sex hormones, in both men and women;
- adequate amounts of other hormones;
- prevention of many diseases, including especially dangerous
Anemia – symptoms, causes, types. How to prevent it and how to treat it? anemia; - Weakened immunity – causes, symptoms and ways to strengthen it
strengthening weakened immunity body.
Vitamin A – a mixture of several valuable compounds
When we talk about vitamin A, we need to know that it is a mixture of several chemical compounds found in the form of carotenoids. There are many of them in nature, but the most important from the point of view of our health include lutein, lycopene and, of course, beta-catorene. These are natural pigments that give color to what we eat, especially fruits and vegetables, so we supply them with our diet and they have antioxidant properties.
Vitamin A was discovered earliest, that is why it received the first letter of the alphabet in its name, and it was isolated by American scientists Elmer McCollum and Marguerite Davis in 1913. It can not only be supplied with food, it is also synthesized on an industrial scale, which made it an ingredient of dietary supplements, such as Hair Care Panda – vitamin jellies perfect for our hair
Vitamin A – natural sources

Despite the appearance on the market of more and more supplements having vitamin A in their composition, its primary source is still the food we eat every day. It is important to properly balance our diet, so we can avoid possible retinol deficiency. The following sources of vitamin A should definitely be on our menu:
- beef, veal and poultry, turkey or chicken breast, duck meat;
- Sea fish, cod, mackerel, hake, herring, tuna;
- freshwater fish, carp, salmon, trout, eel;
- Dairy products, cottage cheese, natural and fruit yogurt, butter, cow’s and goat’s milk, ripened cheese, processed cheese, eggs;
- Offal, especially liver;
- Orange and red vegetables, e.g. carrots, red peppers, tomatoes, pumpkins, red and yellow peppers;
- Other vegetables, spinach, potatoes, green salad, parsley, kale, broccoli, asparagus, green beans;
- fruits, apricots, plums, watermelon, melon, cherries, peaches.
Vitamin A – effects of deficiency or excess and proper dosage
Composing a diet consisting of such a large number of products is a bit cumbersome, so it is always worth having vitamin A supplements on hand, showing effectiveness on many aspects of our health. We should absolutely take care of it if we don’t want to face the ailments caused by retinol deficiency, struggle with avitaminosis. To correctly recognize that we are lacking it, we should know the basic symptoms of vitamin A deficiency, and the most characteristic are:
- impaired vision, a condition called “chicken blindness”, when we see worse after dark;
- weakened immune system resulting in a higher susceptibility to infections;
- skin problems, dryness and cracking of the epidermis;
- other skin conditions, including and
Home remedies for acne – how to win against it without the help of antibiotics acne; - brittle and fragile nails;
- brittleness, fragility and hair loss;
- Gastrointestinal problems, e.g., diarrhea;
- reduced nervous system function;
- menstrual disorders and decreased fertility.
Also be careful not to overdose, which increases the risk of hypervitaminosis, and symptoms of excess vitamin A in the body include:
- headaches;
- muscle and joint pain;
- increased irritability and hyperactivity;
- a constant feeling of fatigue;
- digestive disorders, nausea and vomiting;
- enlargement of certain internal organs, liver and spleen;
- bleeding from the gums;
- persistent itching of the skin;
- photophobia;
- seizures;
- change in skin color, yellowing of the skin;
- reduction of calcium content in bones.
As you can see from the above examples, the basis for the effective effect of vitamin A on our body, is to provide it with a strictly defined dose, differentiated for adults and children, and the recommended ones, which must not be exceeded, are:
Adults:
- Men – 900 µg;
- Women – 700 µg;
- Pregnant women – 770 µg;
- Women while breastfeeding – 1300 µg.
Children:
- 1 to 3 years of age – 400 µg;
- 4 to 6 years of age – 450 µg;
- 7 to 9 years of age – 500 µg;
Adolescents:
- girls 10 to 12 years of age – 600 µg;
- Girls 13 to 18 years – 700 µg;
- Boys: 10 to 12 years of age – 600 µg;
- boys from 13 to 18 years of age – 600-900 µg.
Vitamin A – the most important therapeutic properties
As proven by repeated studies, properly dosed retinol shows numerous therapeutic properties, noticeably improving health, and specialists emphasize above all:
Protection against cancer
Because vitamin A regulates the growth of epithelial tissue, it can prevent the development of skin cancer and other forms of this deadly disease, which attacks various internal systems and organs. Regular consumption of products containing adequate amounts of retinol reduces the risk of the disease by several percent, which is also due to the antioxidant action of this vitamin, which will help slow down the development:
- nasopharyngeal cavity cancer;
- respiratory tract cancer, including lung cancer;
- esophageal cancer;
- colorectal cancer;
- bladder cancer;
- breast cancer.
Prevention of “chicken blindness”
One of the most important uses of beta-carotene is to prevent vision disorders, and a very characteristic symptom of vitamin A deficiency is impaired vision after dusk, the aforementioned “chicken blindness.” Vitamin A is a component of the visual pigment rhodopsin, which determines proper vision. It also prevents the “dry eye” syndrome, which can lead to further damage to the retina and cornea.
These are three more applications of vitamin A, which takes care of strong, shiny hair, healthy, unbreakable nails and skin condition. Retinol is in fact essential for proper metabolic processes taking place in hair follicles and roots . Vitamin A deficiency leads to inhibition of hair growth, making them lose their elasticity, start to crumble and fall out in large amounts.
Healthy skin, hair and nails
Retinol has a similar effect on nails, which not only grow faster but also become less brittle and are always perfectly moisturized, which is why retinol is found in many nail conditioners. As for the skin, it simply cannot do without adequate doses of vitamin A, whichIt penetrates the epidermis and nourishes it from the inside, also reaching the deeper layers of the dermis.
In this way it prevents its cornification, peeling, prevents excessive sweating and sebum secretion, restores firmness, elasticity and natural tone to weakened skin. It also helps minimize the possibility of developing difficult to treat Skin diseases whose symptom is hair loss.
Vitamin A – dietary supplements that contain it
With such a wide range of health-promoting properties of vitamin A, it is used as one of the most important ingredients of many dietary supplements that help relieve the symptoms of various ailments. It is also used in cosmetics, and examples of supplements and cosmetics that have it in their composition are:
Opti Lutein
Tablets against weakened vision, and in addition to properly selected doses of retinol Opti Lutein – restores sharpness to your vision
- marigold extract, full of lutein to improve visual acuity and prevent macular degeneration;
- Bilberry extract, full of natural antioxidants and anthocyanidins to improve microcirculation in the eye;
Zinc – properties. The role of zinc in the body. Zinc paste, or how zinc works on the skin Zinc, also taking care of macular health.

ÉleveRenew
- a unique vitamin complex, in which one of the most important is vitamin A;
- provitamin B5, i.e. panthenol with anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial properties and restoring skin firmness
- glycerine, in a unique formula Glycerin, which moisturizes the skin, smoothes wrinkles and accelerates wound healing;
- hyaluronic acid, protecting the skin against external factors and moisture loss, filling in wrinkles.

Vita Hair Man
This dietary supplement with vitamin A in the formulation counteracts excessive
- vitamin B5, which restores hair color and regulates sebum secretion;
- Vitamin B6, which protects against scalp diseases;
- two amino acids, l-methionine, participating in the synthesis of collagen and l-cysteine, a component of keratin;
- beneficial minerals for hair, zinc and copper.

Sources:
- https://www.healthline.com/health/vitamin-a-for-skin
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/vitamin-a-benefits
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/vitamin-a



