Iron – importance for health, effects of deficiency and excess
Of the many substances necessary for our health, the most important are vitamins and minerals. As for the latter, the one we cannot do without is iron. All deficiencies of this element we must immediately supplement to avoid many health complications, the development of serious diseases that threaten the functioning of almost the entire body.
Contents
What is iron and where does it occur in the human body?
Iron, designated by the symbol Fe in the Periodic Table, which we need to supplement regularly, belongs to a numerous group of mineral elements. Unfortunately, it is found in the human body in small, trace amounts, estimated at a maximum of 3-4 grams. Most of this element is included in hemoglobin, nearly 70 percent; about 10 percent is found in myoglobin, a protein found in muscles.
It is also found in other proteins and in some enzymes that could not perform their function without it. A sizable portion of iron is also in bone marrow, internal organs, spleen and liver, and muscle tissue. Supplied from external sources, it is stored in these aforementioned places and used in many processes inside our bodies. There are two basic types of iron:
- heme iron, the source of which is animal products;
- non-heme iron, which is provided to us by plant products.
Where can we find the most natural iron?
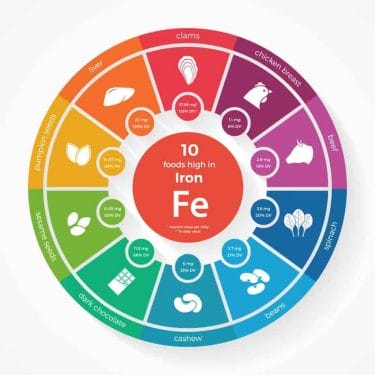
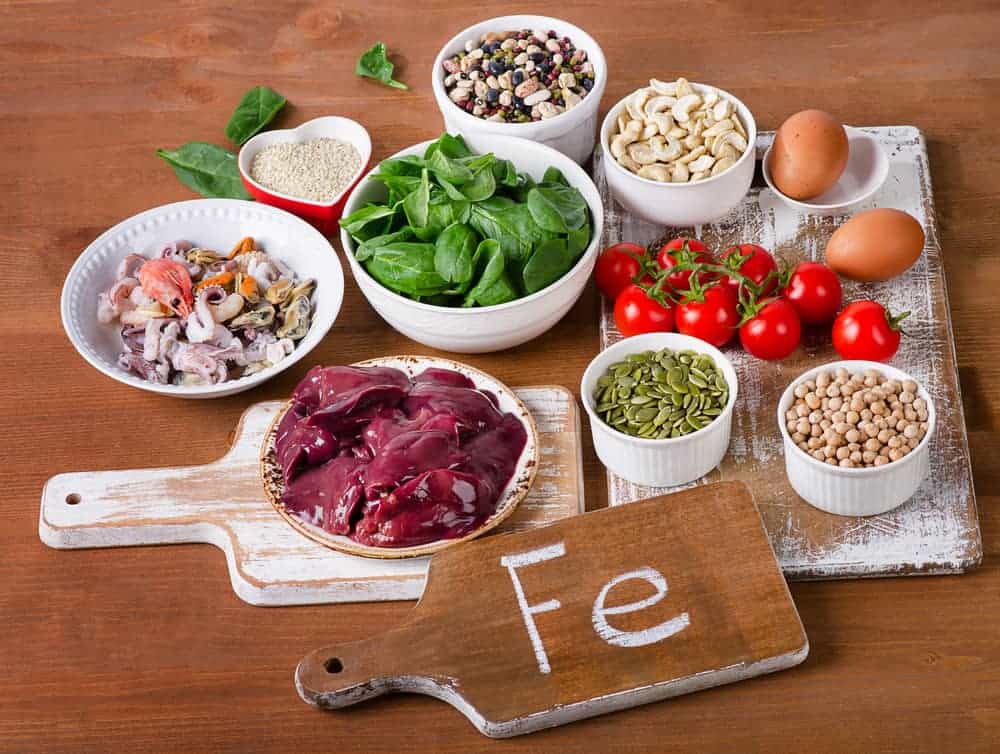
One common way to supplement iron is to properly compose a diet that should include foods containing this element. Most iron is found in the following products:
- offal, liver, pork, poultry, beef and veal, kidneys;
- the well-liked Polish black pudding, one of whose ingredients is pork blood;
- fish, especially sea fish, tuna, mackerel, herring and sardines, both fresh and processed, such as in oil, tomatoes or smoked;
- cereal products, preferably from whole grains, groats, especially millet, wheat bran, wholemeal pasta, wholemeal bread, cereals such as oatmeal;
- pulses, e.g. beans, lentils and chickpeas;
- vegetables, parsley leaves, beets, Brussels sprouts, spinach, potatoes and broccoli;
- fruits, apricots, prunes, fresh and dried, apples and berries;
- pumpkin seeds, poppy seeds and sunflower seeds;
- cocoa beans and dark chocolate made from them;
- nuts, especially pistachios;
- egg yolks;
- spices and herbs, turmeric, sage, fenugreek and cumin.
How much is the recommended daily dose of iron for children and adults?
The peculiarities of how the human body works mean that it cannot assimilate all the iron we supply it with the products listed above. We absorb only about 10 percent of it, and all the rest is unfortunately excreted. There are a number of compounds that significantly impede the absorption of iron, they are contained in numerous products we consume every day such as coffee and tea, influenced by the calcium, magnesium and zinc contained in them.
Others are phytates found in some legumes and polyphenols, found in green tea, among other things, which we drink readily. You should also carefully read the leaflets of the medications you take, and iron absorption can be impaired by supplements with large amounts of magnesium, popular pills used to relieve heartburn symptoms, and some antibiotics.
That’s why it’s so important to supplement its deficiency in carefully selected doses, depending on gender and age, which specialists recommend are:
Children:
- up to 5 months of age – 0.3 mg;
- From 6 months to 1 year of age – 11 mg;
- From 1 to 3 years of age – 7 mg;
- From 4 to 12 years of age – 10 mg.
Adolescents:
- girls from 13 to 18 years of age – 12 mg;
- boys from 13 to 18 years of age – 15 mg.
Adult women:
- 18 to 50 years of age – 18 mg;
- 50 and older – 10 mg;
- pregnant women – 27 mg;
- breastfeeding women – 10 mg.
Adult men:
- 18 years and older – 10 mg.
What are the symptoms and negative effects of iron deficiency and excess?
As with any other substance necessary for the proper functioning of our body, we also need to follow the recommended dosages for iron. If we do not provide it in the right amount or significantly exceed it, we must expect certain health consequences.
Iron deficiency

By far the most common, and most vulnerable to iron deficiency are pregnant women, children, the elderly, professional athletes, people who have lost large amounts of blood , e.g. as a result of an accident or surgery, people who are very overweight, which can be counteracted by taking a dietary supplement Hai Matcha, which has iron in its composition. It is very difficult to notice the first deficiencies of this important element, because the body replenishes it from small reserves accumulated in the above-mentioned parts of the body. Unfortunately, they quickly run out and we begin to feel the alarming symptoms of iron deficiency:
- a constant feeling of fatigue, despite having rested the recommended number of hours;
- lethargy and weakness that can significantly impede normal functioning;
- a feeling of tightness in the chest and shortness of breath;
- palpitations, or an accelerated heart rate;
- elevated heart rate;
- frequent nosebleeds;
- a higher than usual tendency to bruise;
- lack of appetite;
- cold feet and hands;
- brittle and fragile hair and nails;
- pale skin that loses its natural elasticity, which can be restored with the iron-containing Revamin Stretch Mark serum;
- bruises and dark circles under the eyes;
- memory and concentration problems;
- headaches and dizziness.
There are many causes of iron deficiency, but it most often happens to people who do not pay attention to proper nutrition, who can be divided into two groups. In the first, the diet is dominated by everything unhealthy, fast food or highly processed foods, also causing overweight and obesity. The second group are lovers of radical diets, weight loss methods that cause deficiencies in important nutrients, including iron.
Excessive iron
The second situation that can be encountered, also indicating abnormalities, is excessive iron deposition, primarily in the liver. Its symptoms are similar to deficiency at many points, and the most characteristic are:
- fever, in some cases reaching as high as 38-39 degrees;
- chronic states of fatigue;
- sleep problems, which can lead to insomnia;
- stomach complaints, vomiting and nausea;
- rapid weight loss;
- decreased appetite;
- change in skin tone;
- impaired wound healing, caused by blood clotting disorders;
- tinnitus;
- darkness in front of the eyes;
- joint pain;
- decrease in libido;
- irregular menstrual periods;
- loss of hair on the head.
As for the causes of excess iron, specialists mention two in particular. The first again is improper nutrition, and the second is hemochromatosis, a serious metabolic disease. It causes increased absorption of the iron we supply with food through a malfunctioning digestive system and is very difficult to diagnose.
How important is iron to our health?
The importance of iron for health should not be underestimated, unless you want to expose yourself to the ailments and diseases described above caused by a lack or excess of iron. When assimilated in proper doses, it performs a number of extremely important functions, among which it is particularly worth mentioning:
Strengthening the weakened immune system
Our natural protective barrier against the development of infections, inflammation, more or less severe diseases. Any iron deficiency immediately weakens this barrier, making the body more susceptible especially to bacterial infections, and an adequate amount promotes increased production of immune cells.
Participation in the production of red blood cells
One of the main tasks of iron found in the human body is to participate in the formation of erythrocytes, or red blood cells. Without this element, it would be impossible to produce heme, a protein that is an important component of hemoglobin, a co-former of erythrocytes, responsible for binding oxygen molecules and transporting them to every cell in the body. Iron deficiency causes an immediate decrease in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin at the same time, which can lead to the development of microcytic anemia, commonly known as anemia.
Supporting metabolic processes
Metabolism, more commonly known as metabolism, is a complex process that takes place in cells that allows energy to be obtained through the transformation of one substance into another. The energy material can be, for example, excess stored body fat, and the correct course of metabolism allows it to be burned quickly, thus avoiding overweight and obesity.
One of the ingredients that make this possible is precisely iron, which is necessary for the synthesis of various enzymes effective in supporting metabolic functions. It participates in the production of serotonin, called the “hormone of happiness”, thanks to which we control stress, and compoundsconditioning the proper work of the thyroid gland, which produces such important hormones as thyroxine, triiodothyronine and calcitonin.
Beneficial effects on the nervous system
This is another system in the human body that cannot do without adequate doses of iron, greatly improving its work. Thus, it joins other compounds that allow you to enjoy for a long time full intellectual performance, above all, excellent memory and concentration, allowing us to cope with the most difficult mental task.
Strengthen hair and skin health
Iron deficiencies also adversely affect the health and appearance of our hair and skin. If we do not meet the demand for this element, the structure of our hair will be weakened, and it will become thin, brittle, brittle and, as a result, begin to fall out in large quantities. As for the skin, without iron, it will become gray, excessively dry, lose its natural color, be more susceptible to irritation and the appearance of skin lesions, such as acne. Iron, as a powerful antioxidant, also helps remove free radicals that cause it to age faster.
Sources:
- https://www.healthline.com/health/iron-infusion
- https://www.healthline.com/health/pregnancy/iron-rich-foods-for-pregnancy
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/healthy-iron-rich-foods



